Biography
In a career that spanned the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, Auguste Rodin (French, 1840–1917) was deeply inspired by tradition yet rebelled against its idealized forms, introducing innovative practices that paved the way for modern sculpture. He believed that art should be true to nature, a philosophy that shaped his attitudes to models and materials. Many know Rodin for the controversies surrounding his work, such as the scandals around The Age of Bronze or the Monument to Honoré de Balzac, and for his unfinished projects, most famously The Gates of Hell. But few who recognize Rodin's sculptures have failed to be moved by them. His genius was to express inner truths of the human psyche, and his gaze penetrated beneath the external appearance of the world. Exploring this realm beneath the surface, Rodin developed an agile technique for rendering the extreme physical states that correspond to expressions of inner turmoil or overwhelming joy. He sculpted a universe of great passion and tragedy, a world of imagination that exceeded the mundane reality of everyday existence. Although Rodin did not attend the École des Beaux-Arts in Paris, the prestigious school for the training of French artists, his focus on the human form and use of various materials such as bronze, marble, plaster, and clay, illustrate his respect for sculptural tradition and his desire to work within the system for commissions and exhibition opportunities. The hallmarks of Rodin's style—his affinity for the partial figure, his focus on formal qualities and relationships rather than on narrative structure, and his desire to retain the marks of the sculptural process on his finished works—were revolutionary in his time. The evocative intensity of his works were elaborated on by countless artists who followed him, including many who worked in his studio, such as Constantin Brancusi (French, born Romania, 1876–1957) and Aristide Maillol (French, 1861–1944).
Track Auguste Rodin
Get notifications when works come to auction, and access market analytics
Create Free AccountAlready have an account? Sign In
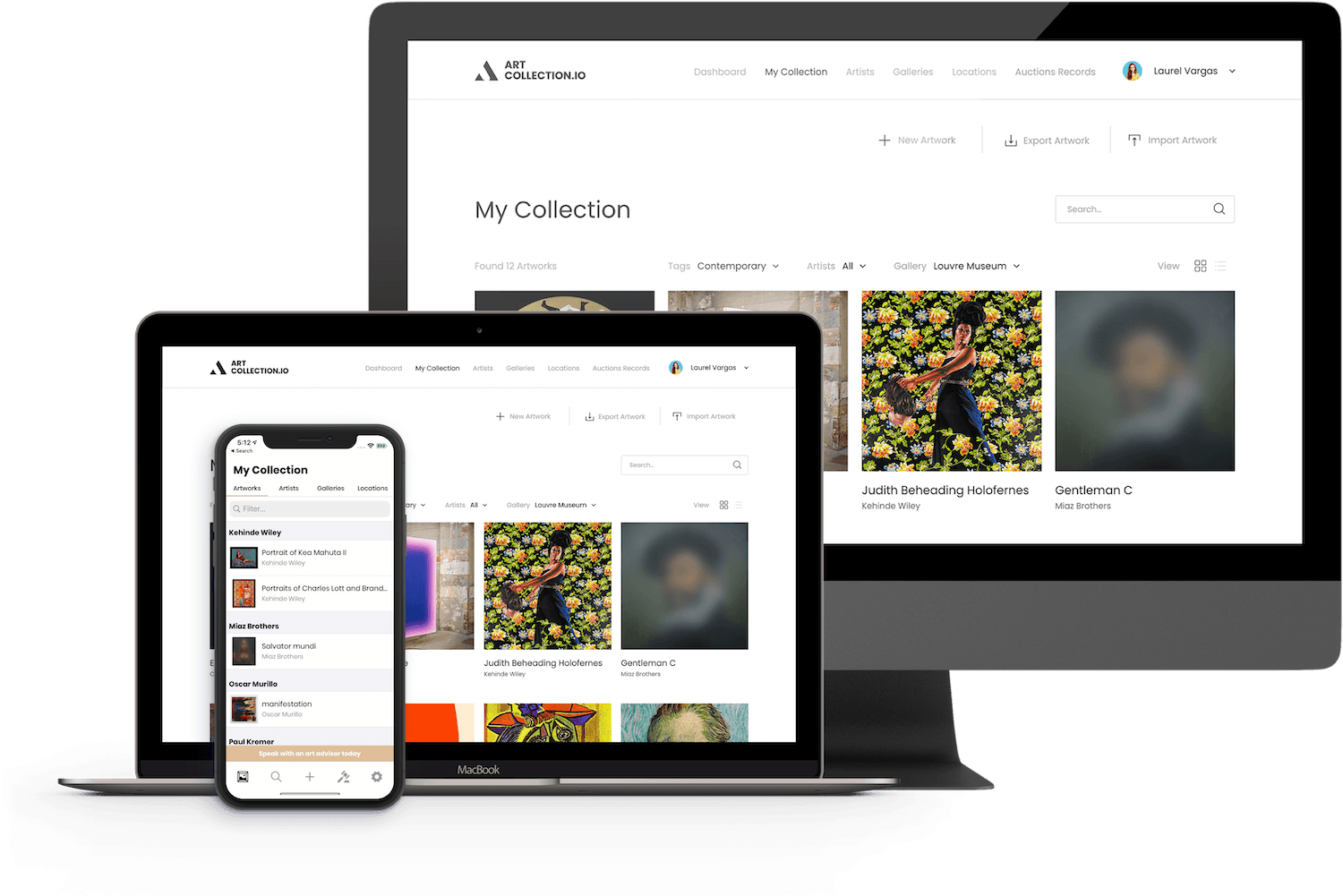
Available on any device, mac, pc & more
ArtCollection.io is a cloud based solution that gives you access to your collection anywhere you have a secure internet connection. In addition to a beautiful web dashboard, we also provide users with a suite of mobile applications that allow for data synchronization and offline browsing. Feel confident in your ability to access your art collection anywhere around the world at anytime. Download ArtCollection.io today!
Biography
In a career that spanned the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, Auguste Rodin (French, 1840–1917) was deeply inspired by tradition yet rebelled against its idealized forms, introducing innovative practices that paved the way for modern sculpture. He believed that art should be true to nature, a philosophy that shaped his attitudes to models and materials. Many know Rodin for the controversies surrounding his work, such as the scandals around The Age of Bronze or the Monument to Honoré de Balzac, and for his unfinished projects, most famously The Gates of Hell. But few who recognize Rodin's sculptures have failed to be moved by them. His genius was to express inner truths of the human psyche, and his gaze penetrated beneath the external appearance of the world. Exploring this realm beneath the surface, Rodin developed an agile technique for rendering the extreme physical states that correspond to expressions of inner turmoil or overwhelming joy. He sculpted a universe of great passion and tragedy, a world of imagination that exceeded the mundane reality of everyday existence. Although Rodin did not attend the École des Beaux-Arts in Paris, the prestigious school for the training of French artists, his focus on the human form and use of various materials such as bronze, marble, plaster, and clay, illustrate his respect for sculptural tradition and his desire to work within the system for commissions and exhibition opportunities. The hallmarks of Rodin's style—his affinity for the partial figure, his focus on formal qualities and relationships rather than on narrative structure, and his desire to retain the marks of the sculptural process on his finished works—were revolutionary in his time. The evocative intensity of his works were elaborated on by countless artists who followed him, including many who worked in his studio, such as Constantin Brancusi (French, born Romania, 1876–1957) and Aristide Maillol (French, 1861–1944).
Track Auguste Rodin
Get notifications when works come to auction, and access market analytics
Create Free AccountAlready have an account? Sign In

Available on any device, mac, pc & more
ArtCollection.io is a cloud based solution that gives you access to your collection anywhere you have a secure internet connection. In addition to a beautiful web dashboard, we also provide users with a suite of mobile applications that allow for data synchronization and offline browsing. Feel confident in your ability to access your art collection anywhere around the world at anytime. Download ArtCollection.io today!


